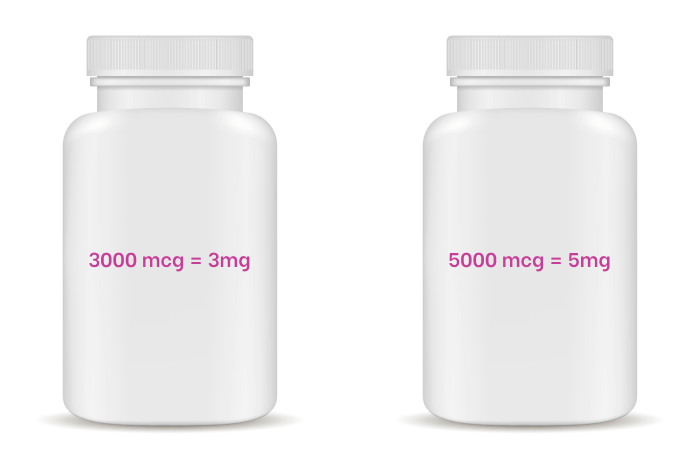Biotin Used to Support Nerve Health
When biotin is taken over time in what’s considered larger doses, it has been found to support better nerve health. In some neurodegenerative diseases, patients may lose the ability to support their myelin with a normal diet. Since D-Biotin is a naturally occurring form of the B vitamin, it has been shown to assist and support in the production of the myelin sheath through a production of fatty acid synthesis.
When myelin, a substance which protects our nerve cells, is damaged, biotin can support key enzymes, prompting the body to produce more myelin. Communication between nerve cells is much easier when there are healthy levels of myelin in the body, and this communication is crucial in supporting nerve health.